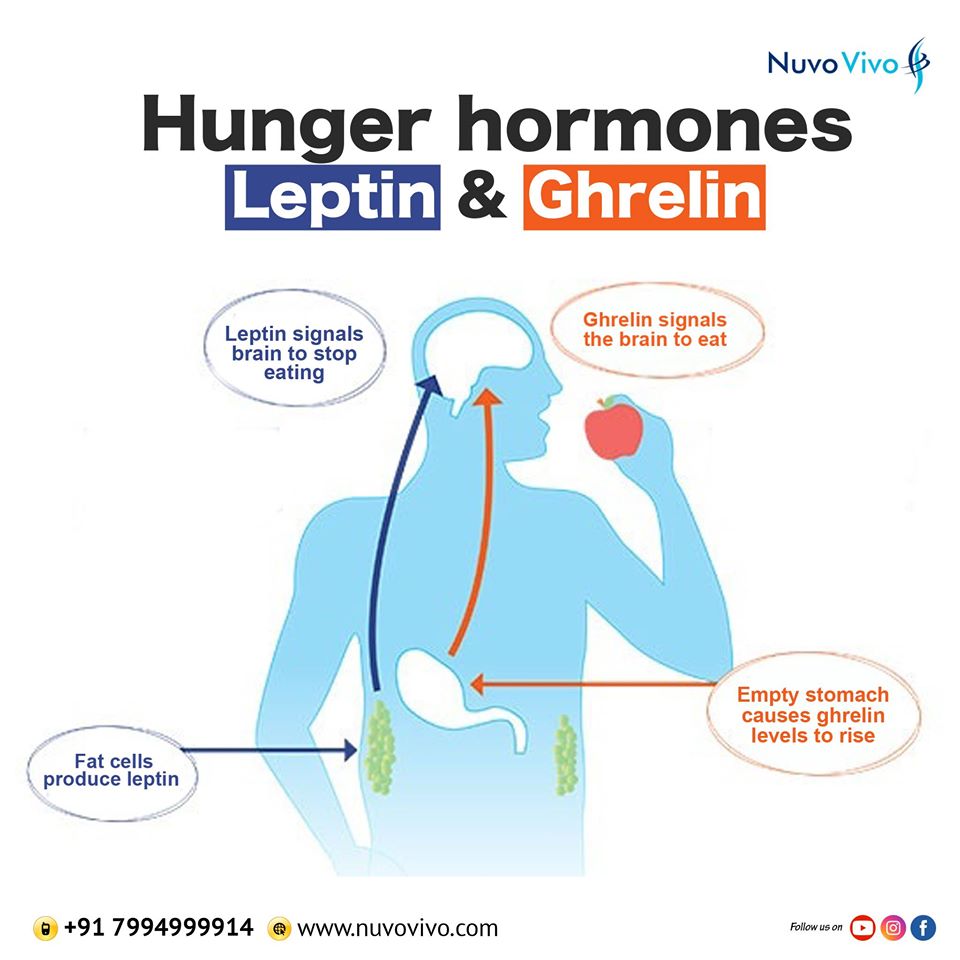
By now, we all know that excess calorie is stored as fat (mostly). We also know that fat is stored in the body as a fuel which can be used in the future. If that is the case, the puzzling question is – why do people who are high in body fat, feel hungry even if they are a bit late to eat??
To explain this, let us introduce to you the hormones that make one feel hungry & full – Ghrelin & Leptin! –
- Ghrelin is produced by the stomach whenever it is empty. This hormone then gets into the blood, reaches the hypothalamus region of the brain and ask the brain to signal the feeling of hunger.. and you eat!
- Leptin, on the other hand, is produced by the fat cells. Leptin signals the brain to make you feel full and not eat anymore! Ideally, higher the fat cells, higher will be the amount of leptin in your body.
However, the interesting thing is that these hormones will do its job just fine if you are not meddling with its working. Often, a person who is overweight has a higher amount of hunger-suppressing hormone (leptin) in the initial stages. But slowly, the receptors to these hormones become resistant and you stop getting the signal of “stop-eating”. i.e your body becomes leptin resistant (like insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes). This is why you still feel hungry inspite of already stored fat in your body.
We had introduced the happy hormone called dopamine that plays with reward-seeking behaviour, in an earlier post. When Ghrelin levels are high, brain signals hunger. As you eat and this hunger is satiated, the happy hormone dopamine is secreted, generating a feeling of happiness and a reward. This is how it becomes a vicious cycle of hunger –> overeating –> reward mechanism!
Similarly, you would also find people who are underweight and malnourished but still doesn’t feel hungry – blame how they have trained their system
The most important thing to do is to never reduce food intake dramatically. Protein takes more time to digest and hence the satiety effect is higher; eating an adequate amount of protein-rich food also helps to suppress the meddling of Ghrelin