Are you constantly feeling fatigued, dizzy, shortness of breath, or any other symptoms of weakness or tiredness?
If yes, be aware, there are chances you may have a condition called anemia, which is a common blood disorder.
Even though it is a very common illness that affects more than 25% of the population worldwide, people hardly talk about it. Most people don’t even know about this blood dysfunction, or sometimes, they confuse this condition with other ailments and often leave anemia untreated.
That’s why we gathered all the essential information you want to know about this blood disorder.
This article will provide an overview of what anemia is, different types of anemia, its symptoms, explain what causes anemia, risk factors of anemia, treatment of anemia, give anemia diet recommendations, and much more. Keep on reading to know further.
What is Anemia?
Anemia is a blood disorder, which happens when your body has a lower-than-normal hemoglobin concentration or a drop in the total number of red blood cells (RBCs).
The term anemia is derived originally from the Greek word ‘anemia’, which means “lack of blood”.
The decrease in the total amount of healthy red blood cells causes lower oxygen levels in your blood than usual, as hemoglobin, the protein inside RBCs, is responsible for carrying oxygen throughout your body.
This below-normal blood oxygen level is the major cause of many of the debilitating symptoms of anemia.
Types of Anemia
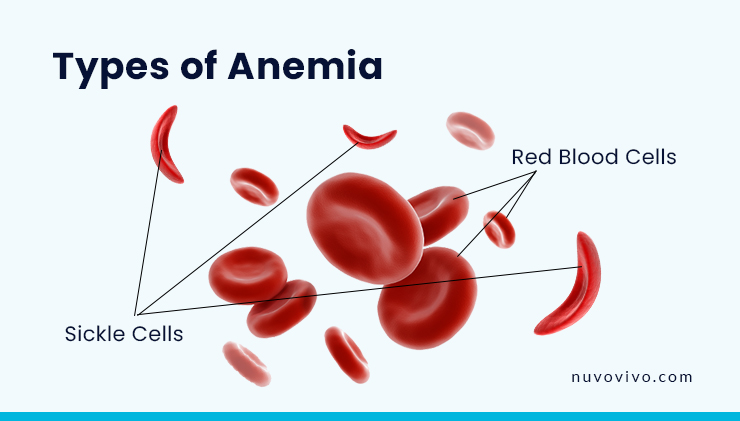
Depending upon the causes, there are myriad different types of anemia, literally over and above 400 forms. Each type may be linked to distinct diseases and disorders. Here are a few of the various types of anemia.
1. Iron Deficiency Anemia (Ferropenic)
This is the most common form of anemia, which happens due to the deficiency of mineral iron in the body. Your body requires iron to produce enough hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen from lungs to organs.
The poor absorption of iron, frequent blood donation, blood loss, menstruation, and inadequate iron intake can be some of the reasons causing a shortage of iron in the body.
2. Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic Anemia, also called Bone Marrow Aplasia, is a rare bone marrow failure condition in which the damaged stem cells in bone marrow fail in producing enough new blood cells.
Autoimmune disorders such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, certain inherited conditions like Shwachman-Diamond syndrome, use of some medication, radiation and chemotherapy treatments, specific viral infections, etc., can injure bone marrow and lead to aplastic anemia.
3. Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell anemia, a type of sickle cell disease (SCD), is a genetic ailment that affects red blood cells.
Usually, RBCs are disc-shaped, but RBCs in a person with SCD contort into a crescent shape resembling a sickle. These sickle cells are rigid and sticky that clog circulation in small blood vessels, causing pain and tissue damage.
4. Diamond-Blackfan Anemia
This congenital form of Pure Red Cell Aplasia is a very rare bone marrow failure syndrome that is typically diagnosed in infants before the age of one. This is a type of anemia in which the bone marrow fails to make adequate red blood cells.
5. Hemolytic Anemia
This form of anemia results when the breaking down of red blood cells (erythrocytes) outruns the production of these cells in the bone marrow.
The process of destruction or rupturing of RBCs is known as hemolysis. If the bone marrow fails to make enough new erythrocytes to recoup the loss, this type of anemia occurs.
Autoimmune disorders, cancers, typhoid fevers, splenomegaly, and other diseases, as well as certain medications, can be the causes of hemolytic anemia.
6. Pernicious Anemia
Pernicious anemia, also known as Addison’s anemia, is a rare disorder that occurs when the body cannot absorb sufficient vitamin B12 (cobalamin) that causes a drastic decrease in the production of healthy RBCs.
A poor diet with low Vit B12, gastrectomy, tapeworm infection, coeliac disease, etc., can cause this condition.
7. Fanconi Anemia
This is a rare but severe blood disorder in the group of inherited bone marrow failure syndromes (IBMFSs), which hinders your bone marrow from making sufficient new blood cells (red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets).
8. Folate Deficiency Anemia
Folate deficiency anemia refers to a type of anemia that results from the deficiency of folic acid, a B vitamin, which prevents your body from making enough red blood cells.
Inadequate intake of folate-rich foods, excessive alcohol consumption, certain medicines such as triamterene and phenytoin, and stomach ailments like celiac disease can be the reasons to develop this type of anemia.
9. Mediterranean Anemia (Cooley’s Anemia)
This condition, also known as Beta Thalassemia Major, happens due to the mutations in the two beta-globin chains of the hemoglobin molecule. This inherited blood disorder affects the hemoglobin production in your body, which in turn leads to anemia.
10. Anemia of Chronic Disease (Anemia of Inflammation)
This type of anemia is multifactorial and can be linked with various underlying disorders, including long-term infections, autoimmune illnesses like rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis and lupus, and chronic conditions such as cancer, kidney diseases, and diabetes.
Symptoms of Anemia
The signs and symptoms of anemia differ based on the cause and severity of anemia. People with mild to moderate anemia may experience minimal or no symptoms. The common symptoms of anemia include:
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Fatigue
- Fast or irregular heartbeat
- Weakness or difficulty concentrating
- Shortness of breath
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Malaise or general discomfort
- Cold hands and feet
- Chest pain
- Headache
- Leg cramps
The symptoms mentioned above are common to various forms of anemia. Following are some other distinct telltale signs associated with specific types of anemia.
People with aplastic anemia may have these symptoms:
- Frequent or prolonged infections
- Fever
- Rashes on skin
- Nosebleed
- Bleeding gums
- Nausea
Anemia caused by the lack of folic acid may experience these symptoms:
- Palpitation (racing heart)
- Appetite loss, which may lead to weight loss
- Lethargy (lack of energy)
- Diarrhea
- Ringing in ears (Tinnitus)
People with iron deficiency anemia may have these symptoms:
- Unusual cravings for ice, soil, paper, or starch (known as pica)
- Tingling or crawling sensation in the legs
- Anemia tongue (swollen, sore tongue)
- Brittle or spoon-shaped nails
The symptoms caused by sickle cell anemia include:
- Painful swelling of the hands and feet
- Delayed growth or puberty in children
- Periodic episodes of pain in the chest, abdomen, and joints
People with pernicious anemia may include these symptoms:
- Lack of appetite
- Loss of reflexes or unusual movements in infants
- Smooth, thick, and red tongue
- Difficulty walking
The symptoms of hemolytic anemia may include:
- Confusion
- Dark urine
- Pain in the upper abdomen
- Jaundice
- Leg ulcers
Causes and Risk Factors of Anemia
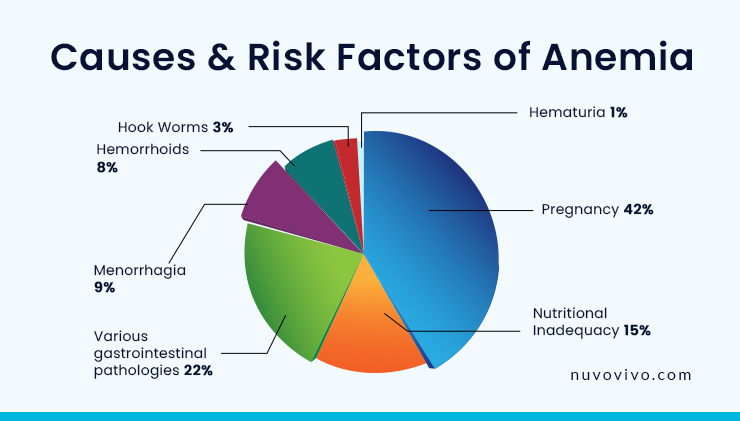
There are different types of anemia that can be caused due to various factors. Unhealthy lifestyle choices can be a major risk factor for developing anemia. But basically, anemia is categorized into three etiologic groups:
- Anemia due to decreased or faulty RBC production
- Anemia due to increased RBC destruction
- Anemia due to blood loss
Common factors that cause a decrease in RBC production
- Insufficient dietary intake of vitamin B12, folate, and iron
- Abnormality in the absorption of nutrients from food
- Hypothyroidism
- Kidney diseases
- Cancer
- Liver cirrhosis
Common factors that cause an increase in RBC destruction
- Autoimmune diseases like lupus
- Enlarged spleen
- Lead poisoning
- Malaria
- Septic blood infection
- Gene inheritance disorders like thalassemia
- Exposure to toxic chemicals
Common factors that cause loss of red blood cells
- Menorrhagia (heavy menstrual bleeding)
- Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding
- Bleeding from UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin and ibuprofen
- Acute Hemorrhage (bleeding)
- Blood loss due to surgery or trauma
Treatment for Anemia

Treatment options for anemia vary depending upon the type of anemia, its severity, and the underlying conditions. Increasing RBCs count is the primary goal behind most of the treatments. Here are some of the treatment options for various types of anemia:
- Iron-deficiency anemia is mainly treated with iron supplements and intake of a diet high in iron. In some cases, iron is also given through IV infusion. If excessive bleeding is what causes the iron deficiency, treat the underlying cause of bleeding.
- Treatments for aplastic anemia include bone marrow transplant (stem-cell transplant), blood transfusions, or medications.
- Vitamin deficiency anemia can be treated with dietary supplements. Vitamin B-12 is administered through injection if you have pernicious anemia. Intake of folic acid supplements can help in Folate deficiency anemia treatment.
- There is no particular treatment for anemia of chronic disease. Treating the underlying disorder is the primary step. Erythropoietin stimulating agents can help in stimulating the production of RBCs.
- The treatment for sickle cell anemia involves intravenous fluids, oxygen therapy, blood transfusions, and pain-relieving medications. Hydroxyurea (Droxia, Hydrea, Siklos), an oral medication, can increase fetal hemoglobin and make the RBCs bigger. A bone marrow transplant is also a treatment option to cure this type of anemia.
- Hemolytic anemia can be treated by plasmapheresis, immunosuppressive therapy, splenectomy, corticosteroid medicines, and treatments for infections.
Diet Plan for Anemia

In the majority of anemic patients, nutritional deficiency is the most common cause, which can be treated and prevented by eating a healthy diet.
Iron-deficiency anemia, vitamin B-12 deficiency anemia, and folate deficiency anemia are among the most common types of nutritional deficiency anemia.
To meet nutritional requirements for the anemic patient, include foods high in iron and other vitamins in their anemia diet, which increases the production of RBCs and hemoglobin in their body.
Below are some of the foods you should include in your diet in order to fight anemia:
- Leafy vegetables like kale, spinach, dandelion greens, collard greens, Swiss chard, watercress, beet greens, etc.
- Fruits such as oranges, pomegranates, lemon, strawberries, etc.
- Meat and seafood, including lamb, red meat, venison, liver, mackerel, oysters, shrimp, salmon, tuna, pompano, chicken, sardines, etc.
- Nuts and seeds such as pistachios, cashews, pine nuts, hazelnuts, sunflower seeds, hemp seeds, pumpkin seeds, etc.
- Beans and pulses, including pinto beans, kidney beans, soybeans, black beans, lima beans, peas, chickpeas, black-eyed peas, etc.
Final Words
A lot of people think of anemia solely as an iron deficiency disease. Most people diagnosed with anemia indeed have low iron levels in their bodies; however, it is only one type of anemia.
As we discussed in this article, there are more than 400 different types of anemia due to various anemia causes. Young children, pregnant women, and people with chronic illnesses are especially vulnerable to develop anemia.
The complications of anemia vary based on the causes and severity. Untreated anemia may lead to complications like depression, tissue hypoxia, restless legs syndrome, pregnancy complications, and heart problems.
So don’t overlook the symptoms of anemia; diagnose and treat at the earliest and lead a healthy lifestyle.
NuvoVivo is an online health, wellness & fitness center that is into medical fitness & lifestyle management. We specialize in transformation (weight loss, muscle gain) and also in managing lifestyle conditions such as diabetes management, cholesterol, thyroid, PCOD and PCOS management, fatty liver, uric acid, hypertension, etc through nutrition & exercises. Our programs are all online, and our clients are from across the world to manage such lifestyle disorders, lose weight, etc. For more details, Contact us at +91 79949 99914

This Post Has 7 Comments
This blog post is worth the read !
Every word of this post is top-notch. Kudos to the author for producing such fantastic content.
The content of this blog is insightful. Keep up the great work!
Your blog post was fantastic, thanks for the great content!
Every time I read a new post, I feel like I’ve learned something valuable or gained a new perspective. Thank you for consistently putting out such great content!
Looking forward to your next post. Keep up the good work!
Pingback: Vitamin B12: Unlocking the Mystery - NuvoVivo: Reverse Your Age & Lifestyle Diseases